
INTRO:
Electric Vehicle Innovations, Electric vehicles (EVs), with Tesla at the forefront of innovation, have revolutionized the automotive industry. These vehicles offer numerous technological advancements that make them stand out from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. Here are ten key tech uniqueness of electric vehicles:
Section 1: Top 10 Good Tech Uniqueness of Electric Vehicles
1. Zero Emissions:
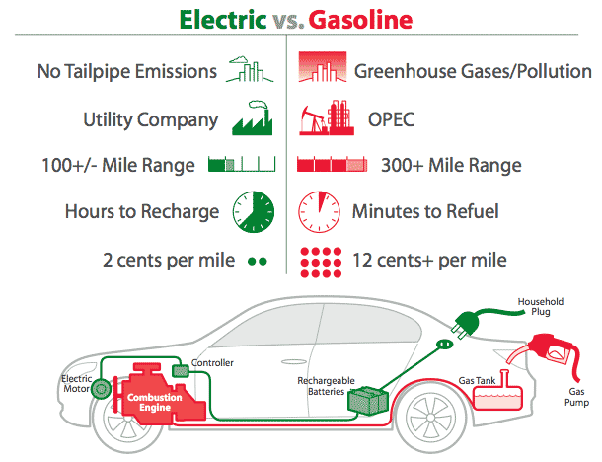
One of the most significant advantages of electric vehicles is their zero-emission nature. Unlike ICE vehicles, which emit harmful pollutants, EVs produce no tailpipe emissions, leading to cleaner air and a reduced carbon footprint.
2. Electric Motors:
Electric vehicles are powered by electric motors that offer instant torque and smooth acceleration. This technology provides a thrilling driving experience and eliminates the need for gear shifting, resulting in a seamless and responsive ride.
3. Regenerative Braking:
EVs employ regenerative braking, a feature that converts kinetic energy into electric energy, which is then stored in the battery. This technology enhances efficiency and extends the vehicle’s range by recharging the battery during deceleration.
4. Longer Range:
With advancements in battery technology, electric vehicles now offer longer driving ranges. Tesla, for instance, has made significant strides in developing high-capacity batteries that enable their cars to travel hundreds of miles on a single charge, reducing range anxiety.
5. Autonomous Driving:
Electric vehicles are at the forefront of autonomous driving technology. Companies like Tesla have integrated advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) that utilize sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence to enable features such as autopilot, lane-keeping, and automatic emergency braking.
6. Over-the-Air Updates:
Tesla has pioneered the concept of over-the-air (OTA) software updates, allowing for remote updates to fix bugs, enhance performance, and introduce new features. This technology ensures that EVs stay up to date with the latest advancements and improvements.
7. Supercharger Network:
Tesla has established a robust Supercharger network that enables fast charging and long-distance travel. This extensive infrastructure alleviates concerns about charging availability and reduces the time required to recharge EVs.
8. Smartphone Integration:
Electric vehicles seamlessly integrate with smartphones, allowing owners to control various functions remotely. Through dedicated mobile apps, users can monitor battery status, pre-condition the cabin temperature, locate charging stations, and even summon their vehicles.
9. Advanced Safety Features:
Electric vehicles prioritize safety and often come equipped with advanced safety features. These include adaptive cruise control, collision avoidance systems, blind-spot monitoring, and intelligent parking assistance, making EVs some of the safest vehicles on the road.
10. Sustainable Energy Integration:
Electric vehicles have the potential to integrate with renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines. This synergy allows EV owners to charge their vehicles using clean energy, further reducing their environmental impact.
Section 2: 5 Negative Effects of Electric Vehicles in the Future
While electric vehicles offer many benefits, it is essential to consider potential negative effects that may arise as their adoption increases. Here are five challenges that may emerge:
1. Battery Production and Disposal:
The production of lithium-ion batteries, which power most electric vehicles, requires significant resources and can have environmental consequences. Additionally, the disposal and recycling of these batteries pose challenges due to their potentially harmful components.

2. Increased Electricity Demand:
Widespread adoption of electric vehicles will impose a substantial increase in electricity demand. This surge could strain the existing power grid infrastructure, requiring substantial upgrades and investments to accommodate the additional load.
3. Raw Material Extraction:
Electric vehicle batteries rely on minerals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. The extraction of these materials can have adverse environmental and social impacts, especially if not carried out responsibly or sustainably.
4. Charging Infrastructure Needs:
As the number of electric vehicles on the road grows, the demand for charging infrastructure will surge. Ensuring an adequate and widespread charging network will require significant investments in infrastructure development, which may take time to implement.
5. Transition and Job Displacement:
The shift from traditional ICE vehicles to electric vehicles may lead to job displacement in the automotive industry. As EV technology advances, the need for certain roles, such as those related to internal combustion engines, may decrease, requiring retraining and job transitions for affected workers.
It is important to note that while these challenges exist, ongoing technological advancements and proactive measures can mitigate their negative impacts, ensuring a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future for electric vehicles.
CONCLUSION…
Electric vehicles bring forth numerous technological advancements and benefits, including zero emissions, advanced safety features, and autonomous driving capabilities. However, challenges such as battery production, increased electricity demand, and job displacement must be addressed to ensure a smooth transition to a sustainable electric vehicle ecosystem. By recognizing these challenges and working towards innovative solutions, we can maximize the positive impact of electric vehicles while minimizing potential drawbacks.